Gynecology
Women through every rhythm of life, from managing PCOS and supporting fertility to caring during pregnancy and guiding hormonal wellbeing in menopause. With a science rooted in empathy, we aim to make every stage a step towards balance and comfort.
Products
- Inofolic HP
- Inofolic Combi HP
- Inofolic phD
- Inofolic Plus
- Inofolic Luteal
- Xyminal
- Delphys
- Delphys Plus
- Aleract
- Aleract HA
- Zyxelle
- Zyxelle Plus
- Eumastós
- Eumastós Gel
- Zoyphen NRT
- Santes
- Ialos
- Pervistop
- Pervistop Foam
- Biguanelle Solution
- Biguanelle Gel
- Biguanelle Ovules
- Emogut
- Emogut Forte
- Synostea
PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome)

PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome)
PCOS is a chronic condition that affects women of reproductive age.
It usually starts during adolescence, but symptoms may fluctuate over time.
Interest in PCOS is constantly increasing due to growing evidence that it goes far beyond being only a reproductive disorder.
PCOS in women of reproductive age up to
Infertility
Infertility
Infertility is defined as “a disease of the reproductive system characterized by the failure to achieve a clinical pregnancy after 12 months or more of regular unprotected sexual intercourse.”
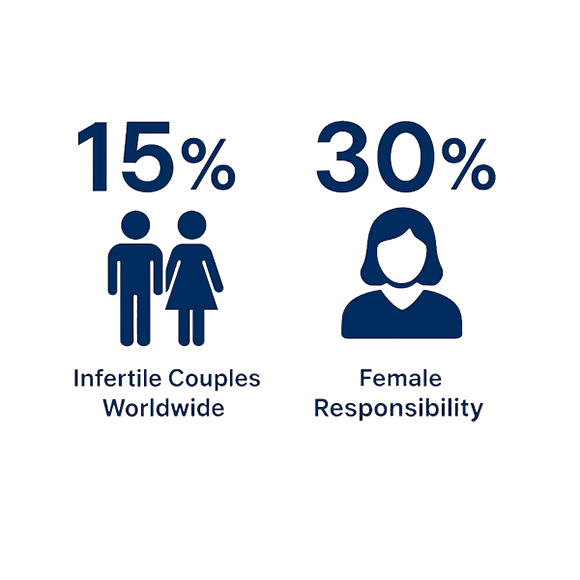
15% of couples worldwide are infertile
Female infertility contributes to 30% of cases
15% — Infertile couples worldwide
30% — Female responsibility
Infertility affects around 70–80% of women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), primarily due to chronic anovulation and hormonal imbalances that disrupt normal ovulatory cycles and compromise oocyte quality.
The most common underlying causes include oligo- or anovulation, tubal obstruction, and implantation failure. Nevertheless, a significant proportion of women experiencing fertility issues still receive no definitive explanation for the origin of their reproductive dysfunction.
Vaginal infections

Vaginal Infections
Vaginal infections represent one of the most common gynecological conditions in women of reproductive age, often resulting from an imbalance in the vaginal microbiota and associated with significant discomfort and reproductive complications
Around 30% of women of reproductive age suffer from bacterial vaginosis or candidiasis. In fact, up to 75% of sexually active women experience at least one episode of symptomatic vaginal candidiasis during their lifetime, and approximately 35% face a relapse during pregnancy.
These infections are among the leading causes of reproductive complications and treatment failure
Menopause

Menopause
Menopausal women currently represent about 26% of the global female population, a figure projected to reach 1.65 billion by 2050.
This transition is accompanied by profound metabolic and physiological changes that significantly affect women’s health and quality of life.
Up to 60% of menopausal women are at risk of developing metabolic syndrome, while around 80% experience vasomotor symptoms such as hot flushes and night sweats. Menopause is also associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, with studies indicating over a 48% rise in disease severity linked to the timing and intensity of menopausal symptoms. Furthermore, bone health is notably impacted: approximately 37.5% of postmenopausal women face an increased risk of developing osteoporosis. These data highlight the importance of early prevention, lifestyle interventions, and targeted therapeutic strategies to support women through the menopausal transition
Osteopenia / osteoporosis
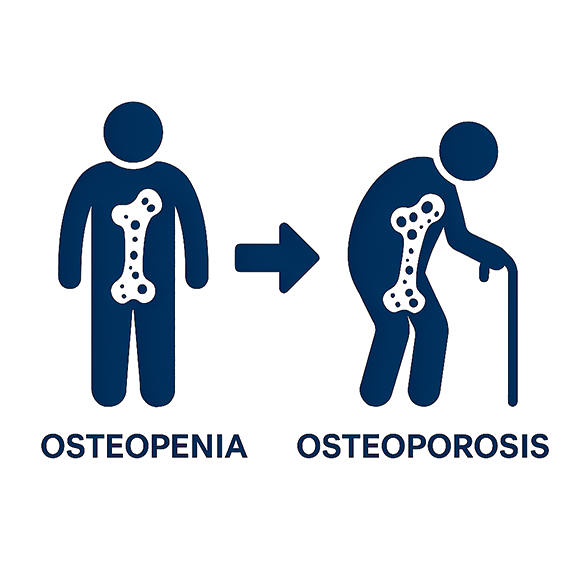
Osteopenia & Osteoporosis
Osteopenia and osteoporosis are progressive conditions characterized by reduced bone mineral density and deterioration of bone microarchitecture, leading to an increased risk of fractures.
Osteopenia represents the early stage of bone loss and is often considered a therapeutic limbo due to the lack of clear guidelines, the variable fracture risk, and the limited or undocumented efficacy of pharmacological treatments.
From an endocrinological perspective, both conditions reflect complex alterations in hormonal regulation—particularly involving estrogen, testosterone, parathyroid hormone, and vitamin D—that critically influence bone remodeling and calcium homeostasis.
Osteoporosis, the more advanced and clinically significant form, places a substantial burden on individuals and healthcare systems. Currently, among people over the age of 55, there are 37 million fragility fractures, equivalent to about 70 fractures every minute.
Overall, osteoporosis affects more than 500 million men and women worldwide, highlighting the global magnitude of this silent yet preventable endocrine-related disease.
Vaginal affections

Vaginal Affections
Vaginal affections are highly prevalent and can arise from multiple causes, including hormonal changes, infections, radiotherapy, or chronic inflammation. Up to 60% of women experience symptoms such as dryness, irritation, or discomfort, while approximately 20% of the overall female population may develop persistent vaginal disorders that compromise quality of life.
These conditions are often accompanied by morphological alterations—such as thinning of the vaginal mucosa, loss of elasticity, and reduced lubrication—that can affect both intimate and daily well-being. Following radiotherapy, the local tissue damage may further aggravate dryness and discomfort, leading to significant physical and emotional distress.
Effective physical and local treatments can play a crucial role in restoring tissue integrity, relieving symptoms, and improving overall comfort and confidence.

